Today in History, July 16, 1885: Sam finishes his book.
Sam had led a bit of a rough life. He saw great success, no doubt, but he was also an alcoholic. His father struggled with the demon for a time, and his grandfather had succumbed to it. In those days they didn’t realize it was often a family trait or a disease…it was simply a weakness. Sam had fought the demon his entire adult life. He was brilliant at is chosen profession. He quit it for a time because of his drinking and tried other jobs…farmer, realtor, shopkeeper…none worked out. As brilliant as he was, he had another weakness; he had a big heart and was much to quick to trust people with his money. So Sam spent most of his life broke.
Even with this, events in his life led him in a round about way to the pinnacle of success. He succeeded where others failed miserably due to his tenacity, his organizational skills and his ability to see the big picture. Yet through it all, no matter how much he achieved, his detractors never forgot, and certainly never let him forget, his demons.
Sam had made his fortune at last…but then, in his older years when there was little to no chance of building success anew, his other failure reared its ugly head again. The people he trusted with his money were scoundrels, and he found himself…and more importantly to him, his family, destitute once again.
Living on borrowed money, things got worse. One day while eating a peach his wife had given him, he felt as if he had been stung by something within it. He had no time for doctors and stubbornly toiled for months until the pain was unbearable to relent to his wife’s demands to see his physician. By then, it was too late. The mouth and throat cancer was advanced, and all that could be done was to provide him with pain killers until the end would come.
Sam’s father had been an inveterate braggart, a schemer and an incessant talker. It embarrassed Sam so that he became the exact opposite. Quiet and humble to a fault, it took everything he had to do what he had refused for years…to blow his own horn and tell his own story. But now it was the only way he could leave his wife and children with a means of support. So he threw himself into the task.
For over a year he wrote. He wore a muffler to cover the baseball sized tumor at his throat. Typical of his demeanor, he never complained of the excruciating pain that wracked him day and night…his family only saw him grimace from the pain when he was asleep and unable to hide it.
Sam worked with a purpose…he amazed his publisher by finishing 10,000 words in a day, written out. Mark couldn’t believe it…Mark was one of the most prolific story-telling authors of his time, and could never match Sam, who disliked the task of telling his own story. But now he had to…for his family…for his legacy because his old detractors were only too happy to repeat their own refrain, “See, we told you so.”
Fighting past the pain and past the fog of his medications, he toiled even when he could no longer write, and tortured himself to dictate his story to others.
Finally on July 16, 1885, Sam completed his autobiography. Mark had promised to publish it for a handsome price which would see to it that Sam’s family did not want for anything. It was suspected that Mark had ghostwritten the work…which he adamantly and angrily denied. His friend Sam had written the work…brilliant and surprising as usual.
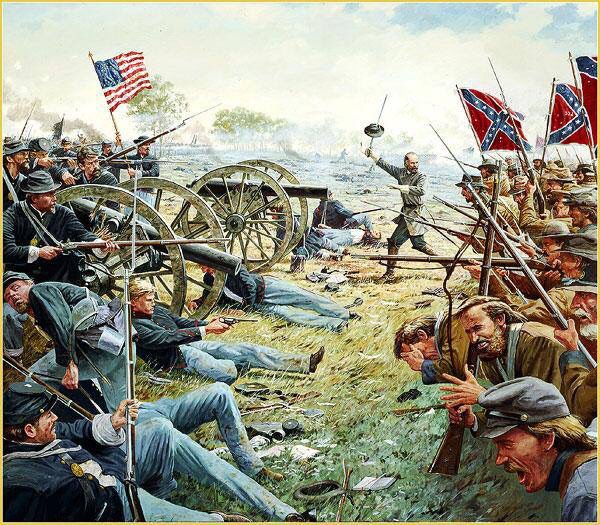
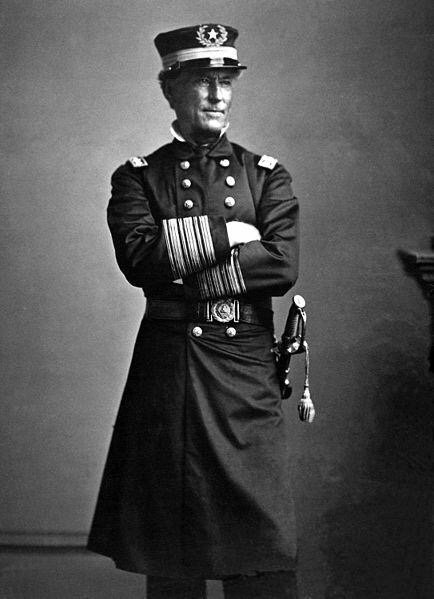
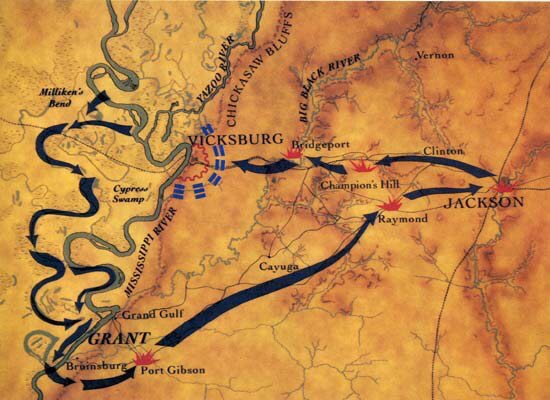
Having won his last battle, he could let go now. Seven days later on July 23, 1885, Hiram Ulysses Grant, “U.S. Grant” due to an Army administrator’s error in his youth, Sam to his friends, a drunk to his detractors, an amazing horseman and hero of the Mexican-American War, General of the Army and President of the United States, passed from this earth.
Mark Twain saw that “The Personal Memoirs of U.S. Grant” was published and the family was treated fairly and well. Sam had found someone trustworthy this time. I’ve read General Grant’s memoirs, and they would be impressive if written by someone in perfect health. They are nothing less that heroic considering the suffering he endured during his final work.