Today in History, February 18, 1862:
“I know you are separated from your people, and perhaps you need funds. My purse is at your disposal.” Union General Ulysses Grant to Confederate General Simon Bolivar Buckner as Buckner prepared to board a river boat taking him north to a Yankee prison.
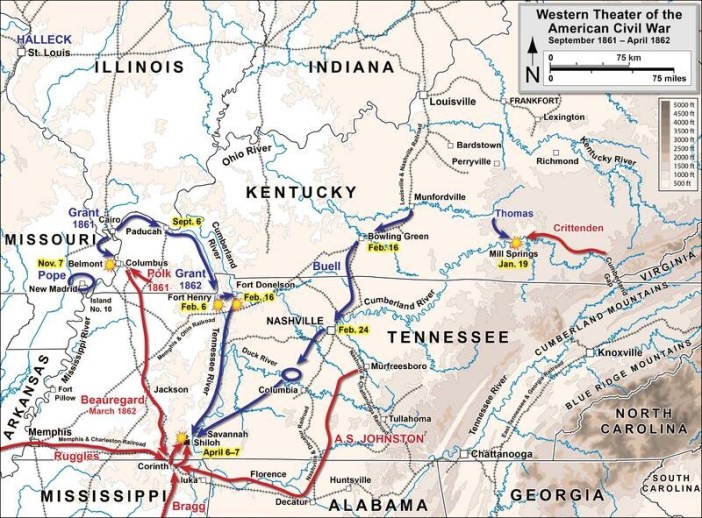
On February 16, 1862 after a hard-fought battle and investment, Confederate Fort Donelson in Tennessee had surrendered to Union forces.
Tennessee was a strategic area in the Civil War, providing resources, people and a launching point to move against the rest of the South.
General U.S. Grant had been little known to the public before this battle, but the victory would change all that. He coordinated with the US Navy to bombard Ft. Donelson and surround the 12,000 men there. After assaults and counter assaults, the Confederate commanders came to the realization loss of the fort was a foregone conclusion, a tragedy for the South.
Gen. Simon Bolivar Buckner was actually third in command. His superiors resigned their positions so they could sneak out and escape. Col. Nathan Bedford Forrest took some of his Cavalry and fled also, leaving Buckner to stay with his men and surrender.
Buckner sent a note through the lines asking Grant for terms. And here is where Grant became famous. He wrote out his response for delivery to Buckner,
“No terms except unconditional and immediate surrender can be accepted. I propose to move immediately upon your works.”
In a time when furloughs and prisoner exchanges were common in battle, Buckner found the response to be “ungenerous and unchivalrous.” Yet he had no choice, his only option was surrender. Having had little but bad news for some time, the Northern papers seized upon the victory.
They used Grant’s initials to rename him “Unconditional Surrender Grant.” Turns out it wasn’t the first time others had changed his name for him, but that’s another story.
The public was finding out something those serving with Grant had learned…he was unpretentious, unceremonious and tenacious. He got results. President Lincoln would eventually say of him, “I can’t spare this man; he fights” in defense of Grant’s reported drinking problem.
If you want History to be more than dates on a page, watch out for the back stories…the facts that bring out the humanity in what you’re reading.
The story reads good already. But lets dig further.
When Grant was younger, he wanted an education. His father worked hard and secured him an appointment to West Point. Initially, Grant didn’t want to go. But once in, he liked it. His uncanny horsemanship impressed fellow cadets and instructors. And he made friends among the other cadets, including Simon Bolivar Buckner, who was attending at the same time.
Grant and Buckner, among many other officers in the US Army, served together and performed heroics in the Mexican-American War of 1846-1848.
After that conflict Grant found himself assigned to the frontier in California, where he missed his family grievously and took to drink. In July of 1854 he suddenly resigned his commission from the Army and sought transport home.
Grant found himself in New York without even enough money to get a meal or pay for a room. And then he happened upon an old classmate and friend, Simon Bolivar Buckner.
The two enjoyed a visit, talked old times and Buckner, who was doing much better financially, paid for his friend’s room and board.
In the intervening years until 1861 and the beginning of the Civil War, Grant was somewhat of a hard luck case. He tried farming, he tried real estate, nothing worked. When the war began he was working for his brothers and his father in a store as a clerk.
When Southern states began seceding many in the US Army that were from those states, resigned their commissions and joined the Confederate Army, including Buckner. Thus the old friends found themselves on opposite sides.
Thus, after the Battle at Fort Dolelson, Grant sought out Buckner before Buckner boarded the boat taking him off to prison in an attempt to return an old favor. Buckner, ever the gentleman, politely refused the return of the kindness.
Grant, of course, would become commander of all Union Armies and eventually President.
Buckner would eventually be exchanged for a Union general officer and continue to serve in the Confederate Army.
He surrendered in New Orleans in 1865 for a second time. He would become Governor of Kentucky among other political successes.
In 1904 he visited the White House and asked President Theodore Roosevelt to appoint his son to West Point. TR quickly agreed.
His son, Gen. Simon Bolivar Buckner Jr would be killed at Okinawa in WWII, the highest ranking officer killed by enemy fire in WWII.